Wondering how does a BMS work? Learn how Battery Management Systems monitor, balance, and protect EVs, smartphones, and energy storage batteries. A beginner-friendly guide.

Batteries are everywhere — in your smartphone, laptop, solar panels, and electric vehicles (EVs). But have you ever wondered what keeps these batteries safe, efficient, and long-lasting? The answer is the Battery Management System (BMS).
In this guide, we’ll explain in simple terms what a BMS is and how does a BMS work, why it’s essential, and how it keeps modern batteries running smoothly.
What is a Battery Management System (BMS)?
Essentially, a rechargeable battery pack’s “brain” is its Battery Management System (BMS). To ensure the battery runs safely and effectively, it is responsible for protecting, monitoring, and controlling it.
Consider it similar to an automobile’s engine control unit (ECU). The BMS keeps an eye on voltage, current, and temperature to maintain the health of a battery, much like the ECU keeps an eye on fuel, air, and temperature to keep the engine operating efficiently.
You’ll find BMS units in:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Renewable energy systems like solar storage
- Consumer electronics such as laptops and smartphones
- Industrial applications like UPS systems and forklifts
Why Do We Need a BMS?
To understand how does a BMS work, let’s first look at why it’s needed.
Batteries are sensitive. If they’re overcharged, overheated, or deeply discharged, they can degrade quickly — or worse, catch fire. Here’s why BMS is so important:
- Safety – Prevents overcharging, overheating, and short circuits.
- Performance – Ensures the battery delivers stable power.
- Longer Lifespan – Protects against conditions that shorten battery life.
- Efficiency – Helps use every bit of stored energy effectively.
Without a BMS, modern lithium-ion batteries would be too risky for everyday use.
Core Functions of a BMS
Before answering “how does a BMS work”, we need to break down its main functions:
1. Monitoring
The BMS constantly tracks:
- Voltage of each cell
- Temperature of the battery pack
- Current flowing in and out
- State of Charge (SOC) – the battery’s level of fullness
- State of Health (SOH) – overall battery condition
2. Balancing
Not all cells in a battery pack charge evenly. If one cell charges faster, it could get damaged.
- Cell balancing ensures all cells share the load equally.
- This maximizes capacity and prevents weak cells from failing early.
3. Protection
The BMS acts like a safety guard. It cuts off charging or discharging if:
- Voltage is too high (overcharge)
- Voltage is too low (over-discharge)
- Current is too high (short circuit or surge)
- Temperature is outside safe range
4. Communication
In EVs and smart systems, the BMS shares real-time data with:
- Vehicle control units
- Charging stations
- User apps or dashboards
This communication helps drivers know the battery’s health, charging speed, and estimated range.
So, How Does a BMS Work? (Step-by-Step)
Now, let’s get to the main question: how does a BMS work?
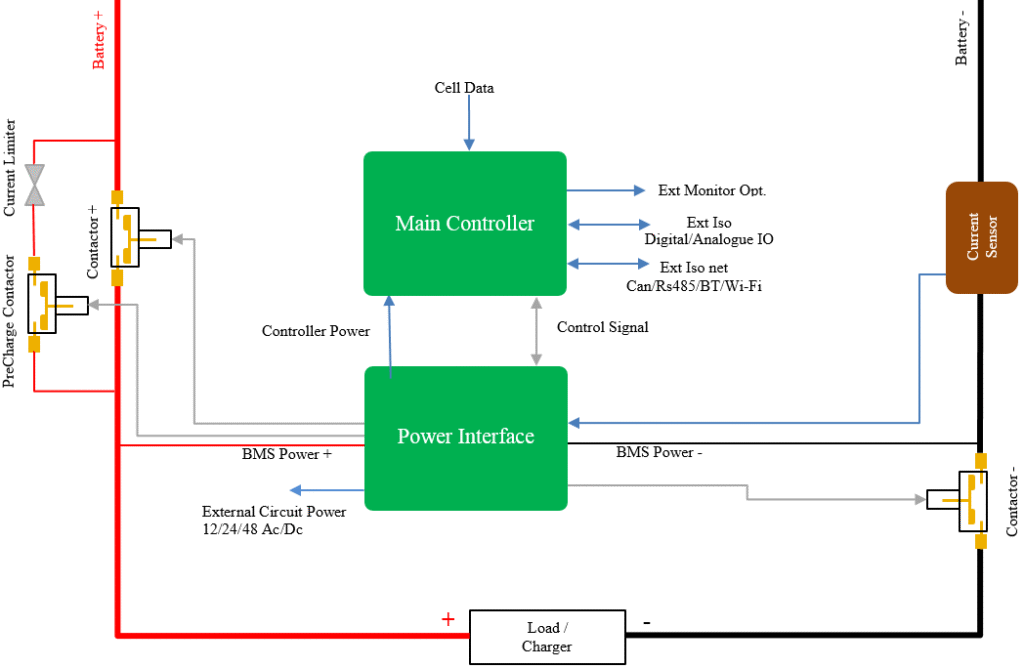
Here’s a simple step-by-step explanation:
- Data Collection – Sensors in the battery pack collect data on voltage, current, and temperature.
- Processing – The BMS’s microcontroller analyzes this data in real time.
- Balancing – If one cell is weaker or stronger, the BMS adjusts charging so all cells remain equal.
- Decision Making – Based on conditions, the BMS allows or blocks charging/discharging.
- Example: If the pack is overheating, it stops charging to avoid damage.
- Communication – It shares key details like battery percentage, charging speed, and health with the user or device.
A BMS, in summary, is a smart traffic controller that makes sure that the energy flow inside the battery pack is balanced, safe, and efficient.
Types of BMS
There’s not just one kind of BMS. Depending on the battery application, there are three main types:
| Type of BMS | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized BMS | One controller for the entire battery pack | Simple, cost-effective | Harder to scale for large packs |
| Modular BMS | Several smaller BMS units connected together | Easy to expand, more reliable than centralized | Slightly more complex than centralized |
| Distributed BMS | Each cell has its own small monitoring circuit | Highest precision, cell-level monitoring accuracy | More expensive to implement |
Real-Life Applications of BMS
Understanding How does a BMS work becomes clearer when you see it in action.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) – Ensures safe charging, maximum range, and long battery life.
- Solar & Renewable Energy Storage – Helps store energy efficiently for later use.
- Consumer Electronics – Keeps your smartphone from overheating or overcharging.
- Industrial Systems – Protects UPS units, forklifts, and grid storage batteries.
Without a BMS, these devices would be unsafe and unreliable.
Challenges Faced by BMS Technology
Even though BMS is powerful, it has some challenges:
- Heat Management – In large EV packs, keeping temperature under control is tough.
- Cost – Advanced BMS designs add to overall battery price.
- Complexity – Designing BMS for large, multi-cell batteries requires advanced engineering.
- Recycling – Managing end-of-life batteries and BMS systems is still evolving.
Future of BMS Technology
The future looks bright for BMS as EV adoption and renewable energy storage rise.
- AI & IoT Integration – Smart BMS that predicts failures before they happen.
- Solid-State Batteries – BMS will adapt to manage safer, next-gen batteries.
- Faster Charging – Advanced BMS will support ultra-fast charging without overheating.
- Recycling Ecosystem – BMS will play a role in second-life battery applications.
Over the next ten years, BMS will develop into an intelligent energy management rather than only a safety device.
Conclusion
So, how does a BMS work? To put it simply, it keeps an eye on, safeguards, balances, and communicates to maintain the safety and effectiveness of your battery. Every modern rechargeable gadget, from smartphones to EVs, depends on a BMS to operate reliably.
The role of BMS will further increase as the world and India transition to electric vehicles and renewable energy. Gaining a knowledge of the fundamentals of BMS allows you to see how intelligent technology powers our everyday lives in the background.
FAQs – Battery Management System
What is a Battery Management System (BMS)?
A Battery Management System (BMS) is an electronic system that monitors and manages rechargeable battery packs and ensures safe operation, optimal performance and long battery life. It monitors voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge of each cell.
How does a BMS work in electric vehicles?
The battery management system (BMS) in electric vehicles continuously checks the temperature and voltage of each cell, distributes the charge among the cells, guards against deep draining or overcharging, and interacts with the vehicle control system to maximize efficiency and security.
What are the main functions of a BMS?
A BMS’s main functions include temperature control, fault detection, charge balancing, cell monitoring, protection against overvoltage and undervoltage, and connectivity with other systems, including vehicle control units.
What are the types of Battery Management Systems?
There are mainly three types of BMS: distributed BMS, where each cell has its own monitoring circuit for high accuracy; modular BMS, which connects multiple smaller BMS units; and centralized BMS, which uses a single controller for the entire pack.
Why is a BMS important in electric vehicles?
For EV batteries to be long-lasting, safe, and effective, a BMS is essential. It maximises battery life and keeps all cells operating at the same level while preventing short circuits, overcharging, and overheating.
Does a BMS affect the battery’s lifespan?
Yes, a BMS is essential for increasing battery life since it keeps balanced charging, makes sure each cell functions within safe bounds, and guards against circumstances that could eventually cause the battery to deteriorate.
Can a BMS be repaired or replaced?
Yes, a BMS can be replaced or repaired based on its design. However, since improper wiring or calibration can result in safety concerns or battery breakdown, it requires for professional expertise.




